How teachers can easily introduce bar model drawing techniques in class
Exploring Bar Model Illustration Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide to Imagining Math Concepts
Bar model attracting methods offer as a useful source for both educators and trainees in picturing mathematical concepts. These models streamline complex mathematical connections, assisting in the comprehension of enhancement, division, multiplication, and subtraction. This guide outlines efficient approaches for applying bar designs, fostering active engagement and real-world connections. As visitors check out the sensible applications and mentor tips, they will discover exactly how these methods can transform their technique to mathematics.
Recognizing the Fundamentals of Bar Version Illustration
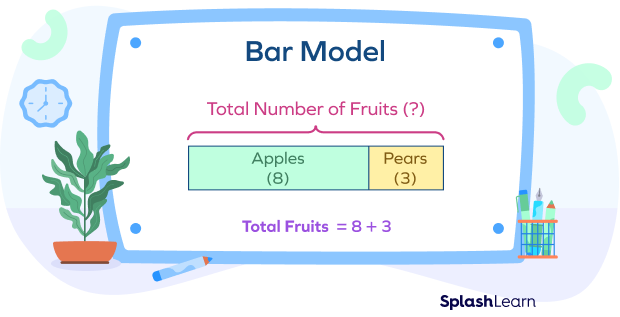
Bar design drawing offers as a powerful visual tool in mathematics, promoting the understanding of numerical partnerships and analytical approaches. This method involves representing numbers and their relationships through rectangular bars, making it easier to envision procedures such as enhancement, multiplication, reduction, and department. Each bar's length represents a specific value, allowing students to compare quantities and recognize proportions plainly.
To develop a bar design, one starts by identifying the trouble's vital elements, typically simplifying right into parts that can be visually represented. In a simple enhancement issue, 2 bars can be drawn, with their sizes standing for the addends. The combined size illustrates the sum. In addition, bar designs can be adapted for extra intricate troubles, consisting of portions and ratios, by readjusting the bars accordingly. Mastering these essentials lays a strong structure for effective problem-solving and deeper mathematical comprehension.
Advantages of Making Use Of Bar Versions in Math
Making use of bar versions in mathematics provides many advantages that improve discovering and understanding. These graphes help pupils in comprehending intricate principles by damaging them down into convenient components. Bar versions give a clear structure for illustrating partnerships between numbers, making abstract concepts extra concrete. They promote a much deeper understanding of mathematical procedures and facilitate analytical by permitting learners to imagine the data they are collaborating with.
Bar versions support the development of critical assuming skills, as pupils have to evaluate and translate the visual details to attract conclusions. This approach encourages energetic interaction with the material, reinforcing retention and proficiency of mathematical concepts. By promoting a strong foundation in visual literacy, bar designs equip students to approach different mathematical difficulties with confidence. Generally, the integration of bar models into mathematics education verifies useful in cultivating both comprehension and logical capacities amongst pupils.
Applying Bar Versions to Addition and Subtraction
Bar designs work as an efficient tool for aesthetically standing for addition and subtraction issues. By highlighting the connection in between numbers, they boost understanding and promote problem-solving. Furthermore, real-life applications of these designs can help students grasp mathematical principles in functional contexts.
Representing Enhancement Aesthetically
When pupils run into addition and reduction problems, aesthetic help can considerably enhance their understanding of these operations. Bar models work as effective devices for standing for addition. By dividing a rectangle right into sectors that correspond to the numbers included, pupils can visualize the relationship in between the amounts. If a pupil requires to include 3 and 5, they can produce a bar separated right into 2 sections: one area standing for 3 and the other representing 5. This clear representation not just streamlines the addition process but additionally reinforces the idea of incorporating amounts. As trainees manipulate these visual aids, they create a deeper understanding of enhancement, causing improved analytic abilities and better confidence in their mathematical abilities.
Reduction With Bar Models
Although subtraction is usually regarded as a more complicated procedure than enhancement, bar designs can efficiently clarify this procedure for students. By aesthetically standing for the amounts involved, trainees can much better comprehend how numbers connect to each other. In a bar model for subtraction, one bar represents the total amount, while another indicates the quantity being deducted. This aesthetic difference assists trainees comprehend the concept of "removing." If a bar reveals 10 devices, and one more bar representing 4 devices is eliminated, pupils can quickly see that 6 devices continue to be. This strategy not only cultivates understanding of subtraction yet additionally help in establishing analytic skills, enabling trainees to visualize their mathematical thinking and improve their total understanding of mathematical principles.
Real-Life Application Instances
Comprehending subtraction through bar models lays a structure for using these strategies in real-life circumstances. In different contexts, such as budgeting or purchasing, individuals can imagine just how much cash remains after expenses. As an example, if a person has $50 and spends $20, a bar model can represent the overall quantity and the spent portion, illustrating that $30 is left. Furthermore, parents can utilize bar models to assist youngsters recognize the number of even more items need to be included in complete a collection, such as having three apples and needing 5. This graph simplifies complex issues, facilitating understanding and retention. Inevitably, bar designs work as effective devices in daily decision-making, improving mathematical understanding in useful situations.
Visualizing Multiplication and Division With Bar Designs
In checking out the application of bar models for multiplication and department, it is important to realize their foundational principles. Constructing reproduction designs permits learners to imagine partnerships in between numbers, while effective department methods can be illustrated via these aesthetic aids. This technique enhances comprehension and problem-solving abilities in maths.
Understanding Bar Designs
Bar designs act as an effective aesthetic tool for illustrating the ideas of multiplication and division. They make it possible for students to represent mathematical connections in a structured style, helping with a deeper understanding of these procedures. In reproduction, bar designs present teams of equal dimension, allowing people to visualize the total quantity when incorporating these teams. On the other hand, in department, bar versions help portray exactly how an overall is separated into smaller sized, equivalent parts, making clear the concept of partitioning. By employing these aesthetic aids, students can understand the underlying concepts of multiplication and division a lot more efficiently. This technique not only boosts understanding but also supports analytical abilities, making bar versions an invaluable possession in mathematical education and learning.
Building Reproduction Versions
Constructing multiplication designs using bar layouts offers a clear method for picturing the process of multiplication. These designs enable learners to represent reproduction as groups of equal components, making abstract concepts extra concrete. To illustrate (3 times 4), a trainee can draw one bar divided into three equivalent segments, each standing for four systems. Furthermore, creating a second bar with the very same length enhances the understanding of duplicated addition, as each segment represents one group. This graph not just aids in understanding reproduction however additionally boosts analytical abilities. By using bar models, students can much better comprehend connections in between numbers and develop a durable structure for a lot more complicated mathematical concepts, resulting in raised self-confidence in their abilities.
Envisioning Department Approaches
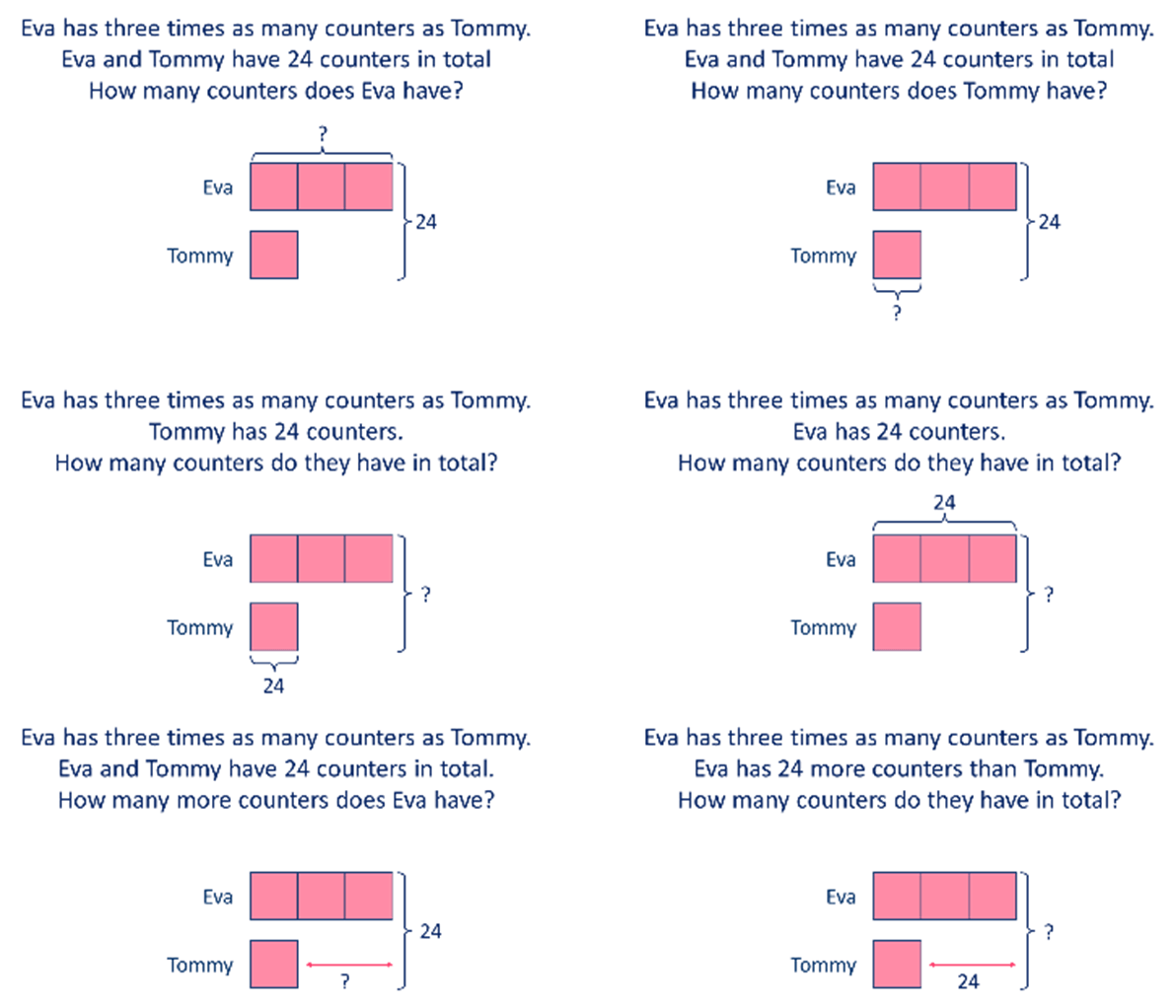
Solving Word Troubles Making Use Of Bar Version Techniques
In a trouble involving enhancement and reduction, trainees can attract separate bars for each amount and after that manipulate them to discover the solution. This process not just clarifies the trouble however likewise cultivates a deeper conceptual understanding. In addition, bar versions can be adapted for different kinds of word issues, making them functional across different mathematical subjects. Inevitably, utilizing bar versions can substantially boost trainees' analytic abilities by offering a clear aesthetic pathway to reach the appropriate response.
Integrating Bar Models in Different Mathematics Topics
Bar designs can be perfectly integrated into numerous math topics, enhancing trainees' understanding of concepts beyond basic arithmetic. In algebra, these aesthetic devices help in standing for equations and inequalities, enabling learners to picture partnerships in between variables. When dealing with geometry, bar designs can show the residential or commercial properties of forms and spatial thinking, assisting students grasp principles like area and boundary successfully. In statistics, bar models facilitate the interpretation of information collections, enabling pupils to compare quantities and recognize trends visually. Additionally, integrating bar models within measurement subjects help in understanding units and conversions by offering a concrete representation of quantities. By using bar models throughout various mathematical locations, instructors can promote a deeper comprehension of complicated concepts, thereby improving problem-solving skills and advertising important reasoning (bar model drawing techniques). This versatility demonstrates the utility of bar models as a foundational tool for trainees in their mathematical trip
Tips for Teaching Bar Designs Properly
Incorporating bar versions into mentor practices requires thoughtful methods to maximize their efficiency. Educators must begin by introducing bar versions with simple, relatable examples that trainees can easily realize. This assists to develop self-confidence and experience with the idea. Progressively enhancing the intricacy of troubles enables learners to use their skills progressively. Furthermore, educators need to motivate pupils to develop their own bar designs, advertising energetic interaction and possession of their learning.
Including collaborative tasks can additionally enhance understanding, as trainees go over and solve troubles in groups. Constant responses is crucial; instructors ought to provide positive discourse on trainees' bar model depictions to direct enhancement. Connecting bar versions to real-life scenarios strengthens their significance, aiding students see the functional applications of their mathematical abilities. By carrying out these techniques, instructors can effectively harness the power of bar designs in their mathematics guideline.
Often Asked Concerns
Can Disallow Versions Be Made Use Of in Other Subjects Besides Mathematics?
Bar versions can certainly be used in different topics past mathematics. They effectively show ideas in scientific research, social research studies, and language arts, assisting to visually stand for partnerships, processes, and ideas for boosted understanding across disciplines.
What Age Team Is Ideal Fit for Learning Bar Models?
Bar models are best fit for youngsters ages 7 to 12, as they develop concrete thinking skills during this period (bar model drawing techniques). At this age, pupils can effectively comprehend abstract ideas via graph and analytic strategies
Are There Digital Tools for Creating Bar Designs?

Exactly How Can I Evaluate Trainee Understanding of Bar Models?
Reviewing pupil understanding of bar designs can entail quizzes, observational assessments, and seminar. Teachers might likewise analyze pupils' completed designs and their capacity to discuss their reasoning, ensuring a detailed assessment of comprehension.
What Are Usual Mistakes When Making Use Of Bar Versions?
Typical errors when using bar designs consist of misstating amounts, failing to properly identify bars, puzzling addition and subtraction, neglecting to utilize consistent scales, and neglecting the value of clear aesthetic splitting up in between various elements.
In enhancement, bar designs can be adjusted for extra complex issues, including portions and proportions, by readjusting the bars appropriately. Subtraction is often regarded as a more intricate operation than enhancement, bar models can successfully clarify this procedure for pupils. In a bar design for reduction, one bar stands for the total amount, while an additional shows the quantity being deducted. If a bar reveals 10 systems, and an additional bar representing 4 units is gotten rid of, pupils can conveniently see that 6 devices stay. When dividing an overall into equivalent groups, pupils can attract a long bar to stand for the whole and then segment it right into smaller bars that indicate each group.